PocketSSH
A portable SSH terminal client for the ESP32-S3 T-Deck Plus handheld device. It provides a full SSH2 terminal with PTY support, hardware keyboard integration, and a graphical interface built on FreeRTOS and LVGL. The project targets secure remote server management on compact, battery-powered hardware.
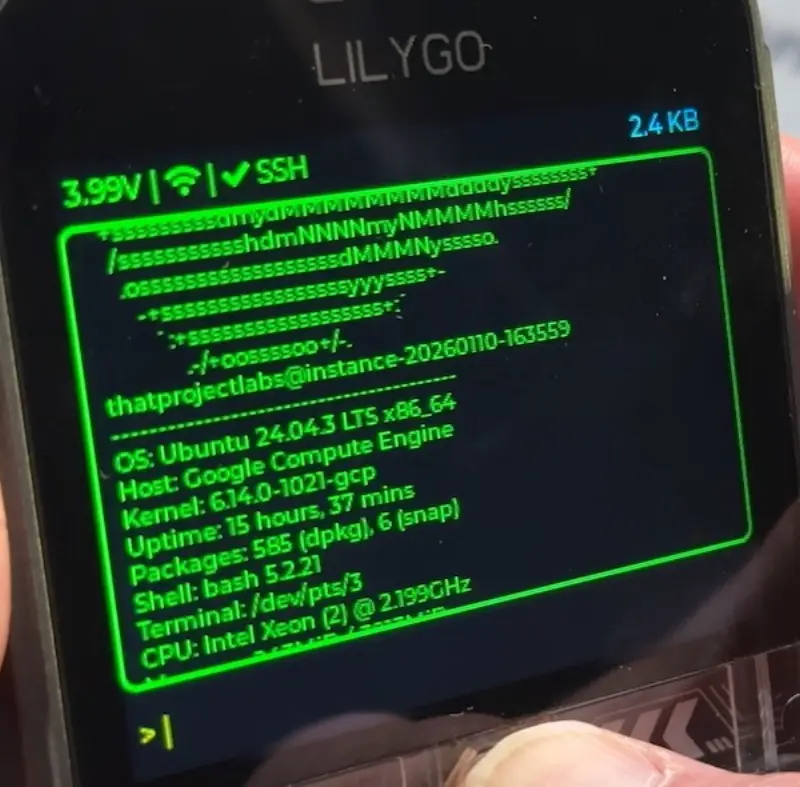
PocketSSH is a specialized terminal client designed to turn the ESP32-S3 T-Deck Plus into a functional, pocket-sized SSH workstation. By combining the secure SSH2 protocol with the unique hardware capabilities of the T-Deck Plus—including its physical keyboard, trackball, and touch screen—PocketSSH enables developers and system administrators to manage remote servers from anywhere.
Hardware-Centric Design
The project is meticulously optimized for the T-Deck Plus hardware suite. It utilizes the C3 keyboard module for full typing capability and a trackball for navigating command history. The visual interface is rendered on a 320x240 color LCD using the LVGL graphics library, featuring connection status icons, battery voltage monitoring, and a real-time byte counter for data transfer.
One of the standout features is the touch-integrated UI. Users can tap the screen to position the cursor or use swipe gestures to toggle a “Special Keys” panel. This panel provides quick access to essential terminal control sequences like Ctrl+C, Ctrl+Z, Tab, and Esc, which are often difficult to trigger on compact physical keyboards.
Technical Architecture
Built on the ESP-IDF v5.5.1 framework, PocketSSH leverages a multi-tasking architecture powered by FreeRTOS to ensure a responsive user experience. The system is divided into several concurrent tasks:
- keypad_task: Processes hardware keyboard input with non-blocking display updates.
- trackball_task: Monitors GPIOs for history navigation, designed to drop input gracefully if the display is busy to prevent lag.
- ssh_receive_task: Handles SSH data reception and terminal output rendering.
- LVGL task: Manages GUI rendering and touch gesture detection.
To maintain performance during high-bandwidth data transfers, the project implements a non-blocking display locking mechanism. By prioritizing screen rendering over input processing during heavy bursts, the system avoids watchdog timeouts and remains stable even when running data-intensive commands like ls -la on large directories.
SSH Implementation via libssh2
At its core, PocketSSH uses the libssh2 library to handle the complexities of the SSH2 protocol. It supports password-based authentication and establishes a secure, encrypted channel for all data transfers. The implementation includes PTY (Pseudo-Terminal) request support with vt100 emulation, ensuring that remote shells behave correctly with standard command prompts and cursor controls.
The connection flow is handled through a series of local commands executed on the device. Users can connect to a local WiFi network and then initiate an SSH session using a simple syntax:
connect <SSID> <PASSWORD>
ssh <HOST> <PORT> <USER> <PASSWORD>Performance and Limitations
While PocketSSH provides a robust terminal experience, it is optimized for standard shell interactions. Due to the 320x240 display resolution and the processing overhead of real-time rendering, the project is best suited for static commands (e.g., cat, grep, df) rather than screen-intensive interactive tools like htop or watch. For text editing, standard editors like nano or vim are functional, though they require more patience than a desktop environment.
Security is a primary focus, with the project utilizing full cipher support (AES, 3DES, Blowfish) provided by libssh2. Future considerations for the project include adding host key verification and public key authentication to further harden the connection process.