YOLOv26n: Optimized QAT & Deployment on ESP32-P4
An end-to-end workflow for Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and deployment of YOLOv26n on the ESP32-P4 SoC. It utilizes the ESP-DL library and a custom dual-head architecture to achieve high-performance, NMS-free inference. The project includes both a Python-based quantization pipeline and an optimized C++ firmware engine.
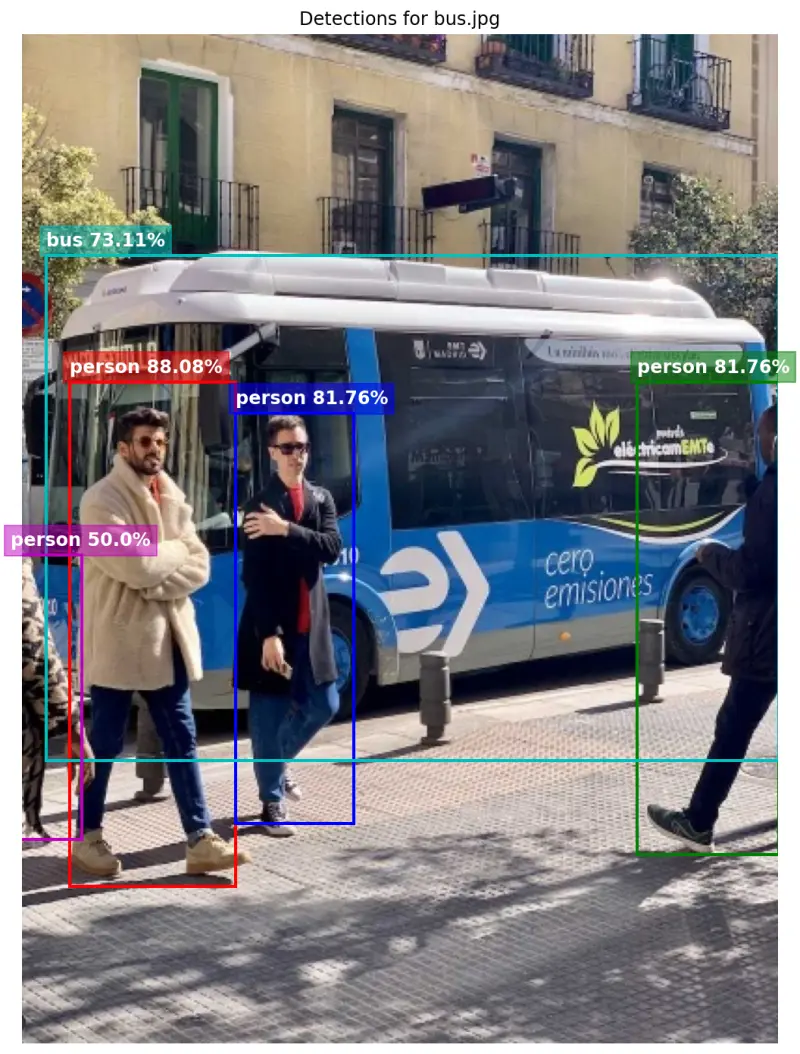
High-Performance Object Detection on the Edge
Deploying sophisticated object detection models on resource-constrained microcontrollers often requires a delicate balance between accuracy and latency. This project addresses this challenge by providing a specialized implementation of YOLOv26n optimized specifically for the ESP32-P4 SoC. By leveraging Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and hardware-specific optimizations, it achieves a significant performance boost over standard baselines.
The implementation stands out by delivering a 30% speedup compared to official ESP-DL YOLOv11n benchmarks, reaching a latency of approximately 1.7 seconds on the ESP32-P4 hardware. This is achieved through a combination of architectural refinements and the use of the ESP-DL library’s high-performance neural network kernels.
Architectural Innovations
The project utilizes a custom dual-head architecture that enables NMS-Free (Non-Maximum Suppression) prediction. By employing a One-to-One prediction head for direct inference, the system eliminates the computational overhead typically associated with post-processing steps like NMS.
Furthermore, the model uses direct regression with RegMax=1. Unlike architectures that rely on Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) with higher RegMax values, this approach reduces output channel complexity and simplifies the post-processing pipeline, making it ideal for the ESP32-P4’s hardware accelerator.
Quantization Aware Training (QAT) Pipeline
To maintain high accuracy while using Int8 quantization, the project includes a comprehensive Python-based QAT workflow. This pipeline, orchestrated via a Jupyter Notebook, handles the entire transition from a PyTorch model to a deployable .espdl artifact. Key features of the quantization process include:
- Custom Export Patches: Modifies Attention modules to use static reshaping, ensuring compatibility with the ESP-DL static graph compiler.
- Sensitive Layer Analysis: Automatically identifies and disables quantization for auxiliary branches to stabilize training.
- PPQ Integration: Uses the
esp-ppqlibrary for graph simplification, fusion, and calibration using methods like KL divergence. - Custom Validation: Includes a validator that simulates quantized graph execution to report realistic on-target mAP metrics during the training process.
Firmware Implementation and Deployment
The firmware component is built using ESP-IDF v5.5+ and is written in C++. It features a dedicated inference engine, Yolo26Processor, which is optimized for ESP-DL’s static graph execution. The firmware supports dynamic resolution switching, with pre-configured support for both 512x512 and 640x640 resolutions.
Deploying the model involves copying the generated .espdl artifacts into the ESP-IDF project structure. The firmware is designed to run on the ESP32-P4 Engineering Sample, taking full advantage of the SoC’s SIMD kernels and hardware acceleration capabilities. This project serves as a robust template for developers looking to implement state-of-the-art computer vision on Espressif’s latest high-performance silicon.