Smart IoT Sensor with XIAO ESP32C6
A power-efficient environmental sensor project built on the XIAO ESP32C6 using the ESP-IDF framework. It supports Wi-Fi and ZigBee connectivity, MQTT messaging, and integrates Bosch BME280/BME680 and Sensirion SGP41 sensors for comprehensive air quality monitoring.
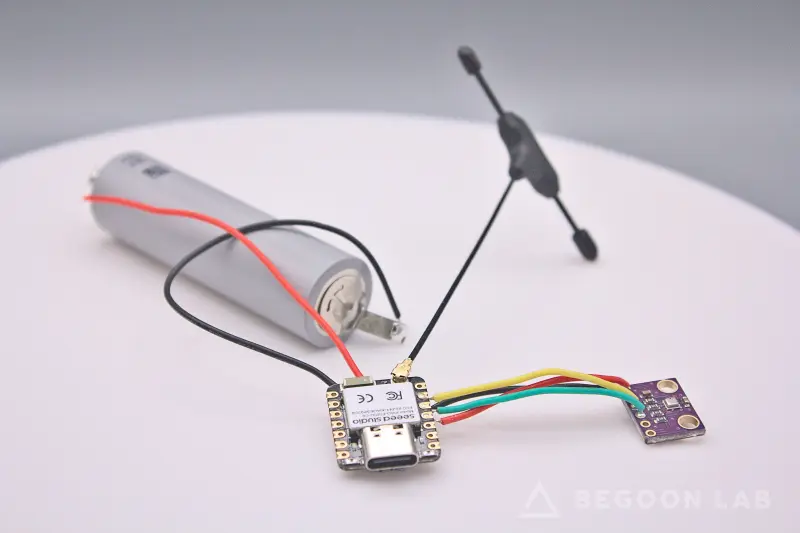
The Smart IoT Sensor is a versatile environmental monitoring device designed for high efficiency and seamless smart home integration. Built around the compact XIAO ESP32C6 board, this project leverages the RISC-V based SoC to provide a robust platform for sensing temperature, humidity, pressure, and air quality. It is specifically optimized for low-power operation, making it suitable for battery-powered deployments in a variety of indoor environments.
Dual Connectivity: Wi-Fi and ZigBee
One of the standout features of this project is its flexible communication stack. Depending on the user’s infrastructure, the sensor can be configured to operate in two distinct modes:
- Wi-Fi & MQTT: In this mode, the device connects to a standard wireless network and publishes sensor data to an MQTT broker. The data is transmitted in a clean JSON format, including fields for RSSI, battery voltage, and connection duration, which helps in monitoring the health of the sensor network.
- ZigBee: For those using low-power mesh networks, the project supports standard ZigBee clusters. This allows the sensor to pair directly with ZigBee coordinators, such as those used in Home Assistant (ZHA or Zigbee2MQTT), appearing as a native environmental sensor.
Environmental Sensing Capabilities
The firmware is designed to interface with several high-quality sensors from Bosch and Sensirion:
- Bosch BME280/BME680: Provides precise measurements of temperature, atmospheric pressure, and humidity. The BME680 adds gas sensing capabilities for broad indoor air quality monitoring.
- Sensirion SGP41: Focuses on VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) and NOx (Nitrogen Oxides) sensing, offering advanced air quality metrics (though currently limited to the Wi-Fi/MQTT path due to ZigBee cluster specifications).
Power Management and Deep Sleep
To maximize battery life, the sensor utilizes the ESP32-C6’s deep sleep capabilities. The device wakes up at user-defined intervals, performs sensor readings, transmits the data via the chosen protocol, and immediately returns to a low-power state. The project also includes a hardware schematic for a voltage divider, enabling the microcontroller to monitor its own LiPo battery voltage and report it alongside environmental data.
Integration with Home Assistant
The project is highly optimized for the Home Assistant ecosystem. For Wi-Fi users, the README provides a comprehensive YAML configuration for MQTT sensors, including device classes and unit measurements. This ensures that once the sensor is active, its data is correctly interpreted for long-term statistics and dashboard visualization. For ZigBee users, the device follows standard commissioning procedures for a “join-and-play” experience.
Hardware and Enclosure
Beyond the firmware, the repository provides a complete mechanical solution. It includes STL files for a custom 3D-printed enclosure designed to house the XIAO board, the sensors, and a LiPo battery securely. The design features a modular assembly process involving a core part, a SoC holder, and a protective wrapper, ensuring the electronics are protected while allowing sufficient airflow for the sensors to provide accurate readings.
Technical Implementation
The project is built using ESP-IDF v5.5.2, the official development framework from Espressif. This allows for fine-grained control over the hardware peripherals and the networking stack. Configuration is handled through the standard idf.py menuconfig interface, where users can set Wi-Fi credentials, MQTT broker details, or switch between Wi-Fi and ZigBee modes without modifying the core source code.