FreeRTOS
202411.00Features
-
Preemptive or co-operative multitasking with priority-based scheduling for deterministic performance.
-
Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) support for multi-core microcontroller architectures.
-
Native TCP/IP stack (FreeRTOS+TCP) with comprehensive support for both IPv4 and IPv6.
-
Integrated TLS v1.3 support via MbedTLS and WolfSSL for secure encrypted communications.
-
AWS IoT integration for Over-the-air (OTA) updates, Device Shadow, and Jobs management.
-
Support for ARMv8-M TrustZone and ARMv8.1-M PACBTI security extensions for firmware protection.
-
Lightweight IoT messaging via coreMQTT and coreMQTT Agent for shared network connections.
-
Cryptographic identity and key management through the corePKCS11 library.
-
Formal verification of software correctness for core libraries using CBMC proofs.
-
Memory Protection Unit (MPU) support for task isolation and enhanced system reliability.
-
Cellular interface library for seamless mobile network integration.
-
SNTP client for accurate network-based time synchronization across devices.
-
Support for 40+ architectures and 15+ toolchains including latest RISC-V and ARMv8-M.
-
Low power modes and tickless idle functionality for energy-efficient battery operation.
-
Trace and profiling support via Percepio View for real-time application analysis.
Architecture
FreeRTOS utilizes a microkernel design focused on providing a minimal but robust set of primitives for real-time applications. The core kernel is responsible for task management, scheduling, and inter-process communication (IPC) through queues, semaphores, and mutexes. It is designed to be highly portable, with a clear separation between the hardware-independent core and the hardware-dependent port layer. This architecture allows it to maintain a tiny memory footprint, typically around 6K to 12K bytes of ROM, depending on the architecture and configuration.
The system is highly modular, following a “kernel + libraries” approach. While the core kernel handles execution, additional functionality such as the TCP/IP stack (FreeRTOS+TCP), MQTT, and security protocols are provided as optional, loosely coupled libraries under the FreeRTOS-Plus umbrella. This design pattern ensures that developers only include the code necessary for their specific application, optimizing resource usage for constrained embedded devices.
Core Components
- Task Scheduler: Supports preemptive, co-operative, and round-robin scheduling with priority levels.
- IPC Primitives: Includes thread-safe queues, binary semaphores, counting semaphores, and recursive mutexes.
- Software Timers: Allows for the execution of functions at specific times or periodic intervals.
- Event Groups: Enables tasks to wait for combinations of events to occur.
- Stream/Message Buffers: Optimized for task-to-task and interrupt-to-task data transfer.
Use Cases
This RTOS is ideal for:
- Industrial Automation: Managing real-time sensor data and motor control loops with deterministic timing requirements.
- Consumer Electronics: Powering smart home devices, wearables, and appliances that require low power consumption and small footprints.
- Medical Devices: Providing a reliable and formally verified foundation for life-critical monitoring and diagnostic equipment.
- IoT Gateways: Handling complex networking stacks, TLS encryption, and cloud connectivity for edge-to-cloud data routing.
- Automotive Systems: Implementing non-safety critical telematics and infotainment systems using ARM Cortex-R or Cortex-A processors.
- Smart Energy: Managing smart meters and grid infrastructure components that require long-term stability and remote OTA updates.
Getting Started
To begin developing with FreeRTOS, it is recommended to clone the main repository using the --recurse-submodules flag, as the kernel and supplementary libraries are maintained in separate Git submodules. Developers should start by exploring the FreeRTOS/Demo directory, which contains pre-configured projects for hundreds of hardware platforms and various compilers (GCC, IAR, Keil). These demos provide a functional baseline that includes the necessary port files and configuration headers (FreeRTOSConfig.h).
Extensive documentation is available on the official FreeRTOS website, including a Kernel Quick Start Guide and a comprehensive API Reference. For community support, developers can access the FreeRTOS Support Forums to interact with the primary developers and the broader ecosystem.
Related Projects
View All Projects →Raspberry Pi Pico W FOTA Example Application
A demonstration project for implementing secure Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA) updates on the Raspberry Pi Pico W. It utilizes FreeRTOS and the lwIP stack to download encrypted firmware images from a TCP server and apply them using the pico_fota_bootloader.
AXP2101 PMIC Driver for ESP-IDF
A specialized port of the XPowersLib library to the ESP-IDF framework for managing the AXP2101 Power Management IC. It provides a comprehensive API for controlling power rails, monitoring status, and configuring voltage outputs on ESP32-based hardware.
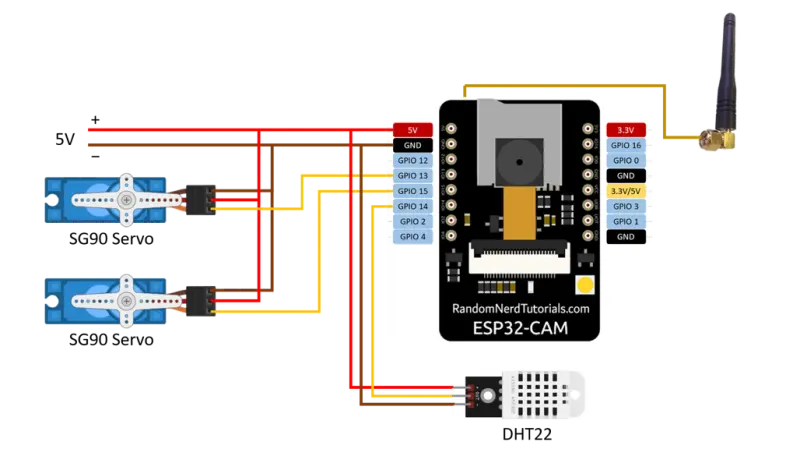
Home Assistant Security Camera with ESP32-Cam
A DIY security camera project using an ESP32-Cam integrated into Home Assistant via ESPHome. It features live video streaming, pan-tilt control using SG90 servos, and environmental monitoring with a DHT22 temperature and humidity sensor.
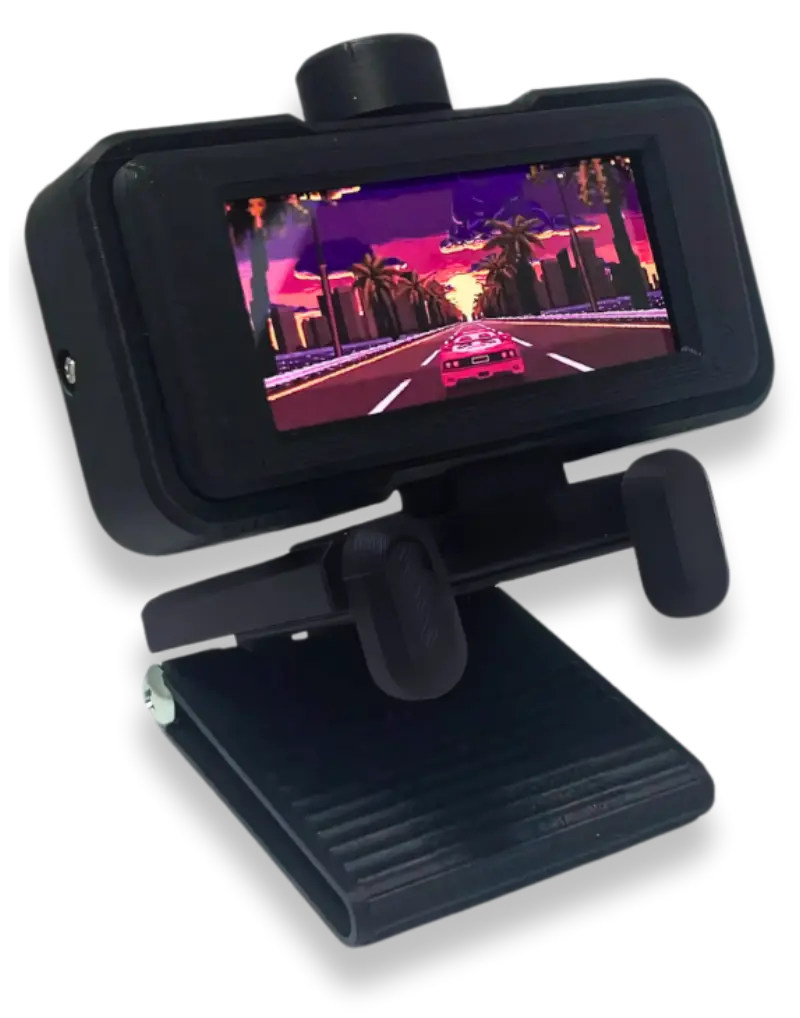

WebScreen Software
An open-source firmware stack for the WebScreen gadget, powered by an ESP32-S3 and an AMOLED display. It integrates the Elk JavaScript engine with LVGL to provide a hackable runtime environment for custom apps, featuring robust WiFi, MQTT, and BLE connectivity.
Wireless 3D Touch Probe Edge Finder for CNC/VMC Machines
A wireless 3D touch probe system for CNC and VMC machines based on ESP32 microcontrollers. It utilizes WLAN UDP communication between a battery-powered sensor probe and a basestation to provide automated edge finding and center detection, specifically designed for machines with automatic tool changers.

ESP32 Marauder for Cheap Yellow Display (CYD)
A specialized port of the ESP32-Marauder firmware tailored for the Cheap Yellow Display (CYD) hardware family. It provides a comprehensive suite of WiFi and Bluetooth testing tools, including wardriving, packet capture, and signal analysis, optimized for various ESP32 and ESP32-S3 touch screen modules.
Kali Zero Firmware (KZFW)
A French-localized firmware for the Flipper Zero based on Xtreme Firmware. It features an enhanced asset management system, a 30-level progression system, and advanced Bluetooth spoofing capabilities for Bad Keyboard attacks.

ESP32-BlueJammer
A 2.4GHz broadband interference tool built for the ESP32 platform using dual nRF24L01+ modules. It targets Bluetooth, BLE, WiFi, and RC drone frequencies for security testing and educational purposes.