Buttfinity
Buttfinity is a modular, customizable button and control system designed for the Gridfinity ecosystem. It utilizes ESP32, ESP8266, and RP2040 microcontrollers to provide functionality as a BLE keyboard, Home Assistant interface, or MIDI controller.
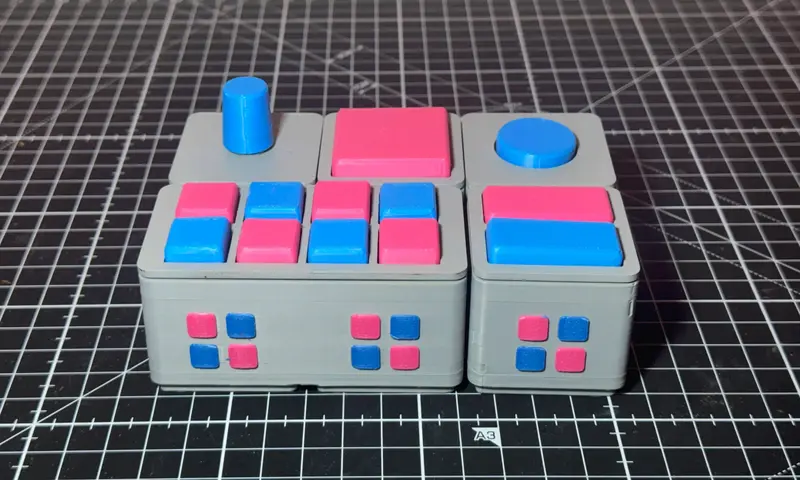
Buttfinity: Bringing Smart Controls to Gridfinity
Buttfinity is an innovative project that merges the world of modular workshop organization with custom embedded electronics. By leveraging the popular Gridfinity standard—a system designed for efficient storage and organization—Buttfinity introduces a way to integrate tactile buttons, sensors, and displays directly into a desktop or workbench grid.
Versatile Hardware Support
The project is designed to be hardware-agnostic, supporting several popular microcontrollers depending on the desired functionality:
- ESP32: Primarily used for creating Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) keyboards, allowing the device to act as a wireless macro pad for a computer.
- ESP8266/ESP32: Ideal for smart home integration, specifically designed to work seamlessly with Home Assistant via the ESPHome framework.
- RP2040: Targeted for use as a wired USB HID device or a MIDI controller, providing low-latency input for creative applications.
Software Integration with ESPHome
One of the standout features of Buttfinity is its accessibility. For the ESP-based versions, the project utilizes ESPHome, a system that allows users to create custom firmware through simple YAML configuration files. This means that users can deploy complex smart home buttons or BLE macro pads without needing to write traditional C++ code. The project documentation provides clear paths for setting up these devices, whether the goal is to trigger Home Assistant automations or send keyboard shortcuts to a PC.
Modular Mechanical Design
The physical components of Buttfinity are built using OpenSCAD, a programmer-centric 3D modeling tool. This allows the bins and lids to be parametric and highly customizable. The repository includes models for various configurations, such as:
- Mechanical switch lids (compatible with Cherry MX style switches).
- Touch sensor housings.
- OLED display mounts.
- Baseplates and bins that adhere strictly to the Gridfinity specifications.
The use of the BOSL2 library in the OpenSCAD files ensures high-quality, reliable geometry for 3D printing. For those who prefer ready-to-print files, the project also provides pre-exported STLs and print profiles on MakerWorld.
Expanding Capabilities
While the project is currently a work in progress, it already outlines an ambitious roadmap for future sensor integration. The Sensors.md file lists several planned modules, including:
- Environmental Sensing: BMP280 for temperature and pressure.
- Distance & Motion: VL53L0X laser sensors and LD2420 radar modules for presence detection.
- Visual Feedback: 0.96” OLED screens and WS2812 LED rings for status indicators and lighting effects.
Getting Started
To build a Buttfinity module, users typically follow a workflow of printing the desired Gridfinity-compatible bins, soldering the chosen microcontroller to the switches or sensors, and flashing the firmware using the provided ESPHome configurations. The project emphasizes a “no programming necessary” approach for the software side, making it an excellent entry point for makers who are comfortable with a soldering iron but may be intimidated by complex firmware development.
By combining the organizational logic of Gridfinity with the power of modern microcontrollers, Buttfinity offers a unique, expandable solution for anyone looking to add custom, tactile controls to their workspace.