Arduino DroneCAN
A library for integrating sensors with Ardupilot and PX4 via the DroneCAN protocol using the Arduino framework. It abstracts the DroneCAN layer to simplify message handling on STM32-based hardware like the Beyond Robotix CAN node series.
Overview
Arduino DroneCAN is a specialized repository designed to simplify the integration of sensors and peripherals into the DroneCAN ecosystem. DroneCAN (formerly known as UAVCAN v0) is the primary CAN bus protocol used by popular open-source flight stacks like Ardupilot and PX4. While DroneCAN is powerful, implementing it from scratch or integrating it into a custom sensor can be a daunting task due to the complexity of the Data Structure Description Language (DSDL) and the low-level CAN handling required.
This project provides an abstraction layer that allows developers to use familiar Arduino libraries for their sensors while the library handles the heavy lifting of the DroneCAN protocol. It is particularly useful for developers who want to create custom CAN nodes without the overhead of the full AP_Periph codebase, which, while powerful, can be complex to modify for simple one-off sensor integrations.
Key Features
The library is more than just a simple message wrapper; it provides a complete set of features required for a production-ready DroneCAN node:
- Message Handling: Easy-to-use functions for sending and receiving standard DroneCAN messages.
- Node Management: Automatic handling of standard DroneCAN requirements, including node allocation and node info reporting.
- Parameters: Support for DroneCAN parameters, allowing users to configure the node directly from flight controller ground control stations like Mission Planner or QGroundControl.
- Firmware Updates: Support for firmware updates over CAN, enabling remote maintenance of the node once it is installed on a vehicle.
Technical Architecture
The repository is built on a foundation of proven open-source components. It utilizes libcanard, a compact implementation of the DroneCAN/UAVCAN protocol in C, which is ideal for resource-constrained microcontrollers. The project also includes pre-generated DroneCAN message types, saving developers from having to run the DSDL compiler manually.
For the build system, the project leverages PlatformIO, providing a structured environment for managing dependencies and board configurations. It includes custom Python scripts for post-build actions, such as append_crc32.py, which adds ArduPilot-compatible firmware descriptors and CRC checks to the binary, ensuring compatibility with standard bootloaders.
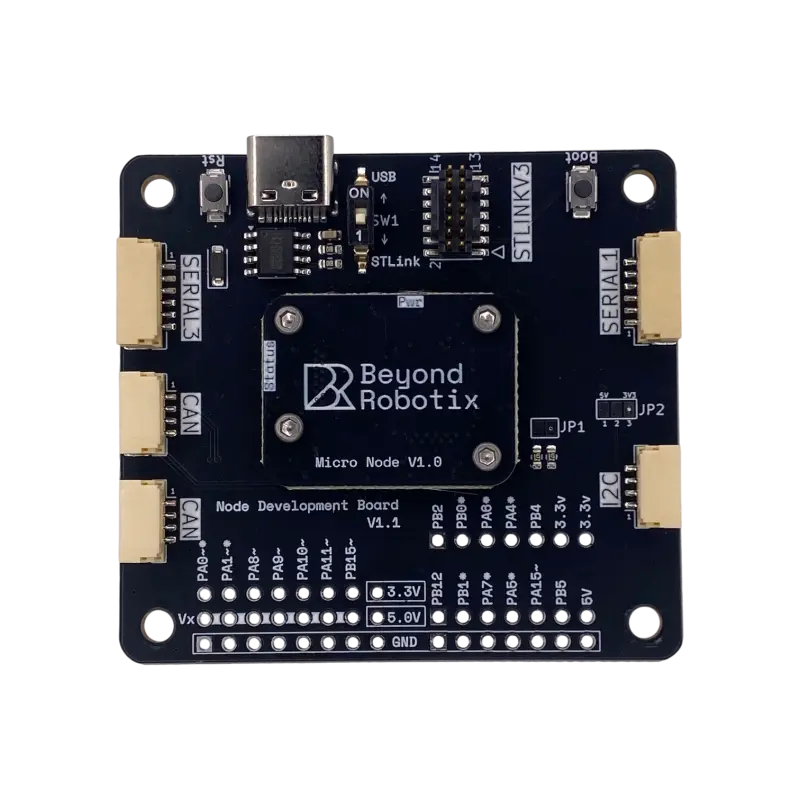
Hardware Support
While the library is designed to be portable across the STM32 ecosystem via the Arduino Core, it is pre-configured for the Beyond Robotix CAN node series. Supported hardware targets include:
- MicroNode: Based on the STM32L431 microcontroller, offering a balance of low power and sufficient performance for most sensor tasks.
- CoreNode: Utilizing the high-performance STM32H743, suitable for more demanding applications requiring CAN FD support.
- MicroNode Plus: Featuring the STM32H723 for advanced processing capabilities.
Getting Started
Integrating a sensor typically involves initializing the DroneCAN library and then calling a simple send function within the main loop. For example, sending battery information is reduced to a few lines of code:
uavcan_equipment_power_BatteryInfo pkt{};
pkt.voltage = analogRead(PA1);
pkt.current = analogRead(PA0);
sendUavcanMsg(dronecan.canard, pkt);The repository structure is designed for immediate use, with an example application provided in the src/main.cpp file. Developers can clone the repository, open it in PlatformIO, and begin flashing their hardware instantly. For those needing custom messages, the project includes instructions and scripts for generating new headers from DSDL definitions using the dronecan_dsdlc tool.