Tensorflow Micro
v2.21.0Features
-
Comprehensive ecosystem for machine learning research and production deployment.
-
Stable Python and C++ APIs with additional support for Java and JavaScript.
-
High-level Keras API for fast prototyping using sequential, functional, and subclassing models.
-
Eager execution for immediate operation evaluation and simplified debugging.
-
Graph execution via tf.function for optimized performance and cross-platform portability.
-
Automatic differentiation using tf.GradientTape for building complex neural network architectures.
-
Flexible data input pipelines using the tf.data API for efficient multi-threaded preprocessing.
-
Distributed training support across multiple GPUs, machines, and Tensor Processing Units (TPUs).
-
XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) compiler for optimizing and JIT-compiling computation graphs.
-
Comprehensive visualization and debugging suite through the TensorBoard toolkit.
-
Model optimization tools including magnitude-based weight pruning and post-training quantization.
-
Native support for mobile and edge devices via the lightweight TensorFlow Lite solution.
-
Production-grade model serving and lifecycle management through TensorFlow Extended (TFX).
-
Extensive library of pre-trained models and components available via TensorFlow Hub.
-
Specialized modules for probabilistic reasoning, reinforcement learning, and ranking algorithms.
-
GPU acceleration support for CUDA-enabled cards on Ubuntu and Windows systems.
-
Device plugin support for hardware-specific acceleration on DirectX and MacOS-metal.
-
Official Docker containers for simplified environment setup and reproducible builds.
Architecture
TensorFlow is built on a multi-layered architecture designed for flexibility and high-performance computation. At its core is a distributed runtime engine that handles the execution of computational graphs across various hardware backends. The framework supports two primary execution modes: Eager Execution, which evaluates operations immediately for an intuitive development experience, and Graph Execution, which uses the XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) compiler to optimize computations for production environments. This dual approach allows developers to transition seamlessly from research to high-scale deployment.
The system is organized into several key subsystems that interact to manage the ML lifecycle. The Keras API serves as the high-level interface for model definition, while tf.data manages complex input pipelines. Below these, the core C++ engine interfaces with hardware-specific libraries like CUDA for NVIDIA GPUs or the XLA compiler for TPUs. The architecture also includes a Device Plugin mechanism, allowing third-party hardware providers to integrate specialized accelerators like DirectX-based GPUs or Apple’s Metal framework without modifying the core codebase.
Core Components
- Keras: The high-level API for building and training deep learning models.
- tf.data: A library for constructing complex input pipelines from diverse data sources.
- XLA: A domain-specific compiler for linear algebra that optimizes TensorFlow computations.
- TensorBoard: A suite of visualization tools for inspecting and understanding model runs.
- TensorFlow Lite: A dedicated engine for deploying models on mobile and embedded devices.
Use Cases
This library is ideal for:
- Deep Learning Research: Developing and testing new neural network architectures using flexible subclassing and custom training loops.
- Computer Vision: Implementing image classification, object detection, and segmentation models for real-time applications.
- Natural Language Processing: Building transformers and sequence-to-sequence models for translation, sentiment analysis, and text generation.
- Production ML Pipelines: Deploying scalable machine learning models using TFX for data validation, training, and serving.
- Edge Computing: Optimizing and running models on resource-constrained hardware like Android devices and Raspberry Pi.
- Reinforcement Learning: Training agents to solve complex decision-making tasks using the TF-Agents library.
- Probabilistic Modeling: Combining deep learning with probabilistic reasoning using TensorFlow Probability.
Getting Started
To begin developing with TensorFlow, the easiest method is to install the library via the Python package manager. For standard CPU and GPU support on Linux and Windows, use pip install tensorflow. For users requiring specific CUDA configurations, the tensorflow[and-cuda] package is recommended. Developers can immediately verify their installation by importing the library and performing basic tensor operations, such as tf.add(1, 2).
Comprehensive documentation, including beginner and expert tutorials, is available at tensorflow.org. For interactive learning, Google Colab provides a hosted Jupyter notebook environment that requires no local setup and offers free access to GPU and TPU resources. Detailed API references for Python, C++, and other supported languages can be found in the official API Documentation.
Related Projects (16)
View All 16 Projects →
Silicon Labs Arduino Core
An Arduino core implementation for Silicon Labs microcontrollers, enabling support for Matter, BLE, and low-power wireless applications. It provides a comprehensive set of libraries and drivers for EFR32 and MGM24 series hardware, integrating Silicon Labs' Gecko SDK and FreeRTOS for advanced protocol stacks.

STM32 AI Model Zoo Services
A comprehensive suite of Python scripts and services designed to facilitate the end-to-end integration of AI models onto STM32 microcontrollers and microprocessors. It supports PyTorch, TensorFlow, and ONNX frameworks, providing tools for training, quantization, benchmarking, and automatic application code generation for various computer vision and audio use cases.
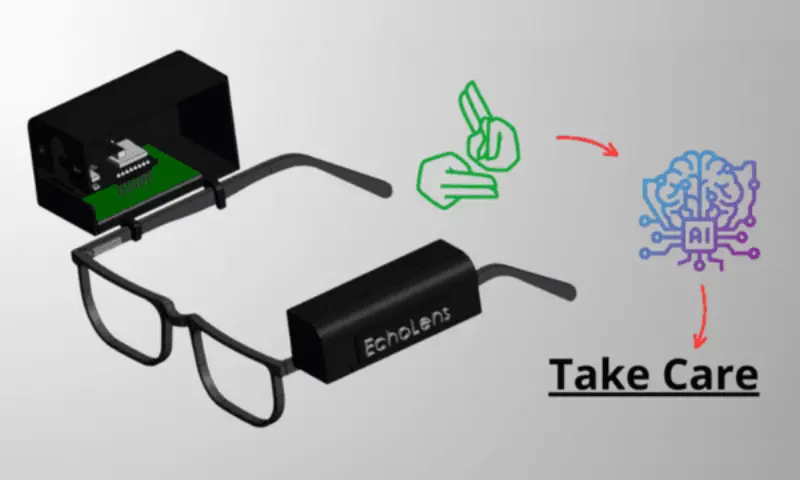
EchoLens: AI-Powered Smart Glasses
An ESP32-CAM based assistive technology project designed for the deaf and mute community. It leverages AI to provide real-time speech-to-text conversion and American Sign Language (ASL) to speech translation, integrated into a wearable smart glasses form factor.

ESPHome Meter Reader TFLite Component
A modular framework for running TensorFlow Lite Micro models on ESP32 devices within the ESPHome ecosystem. It provides specialized components for digital and analog meter reading, image processing, and active learning data collection, optimized with ESP-NN for high-performance edge AI.
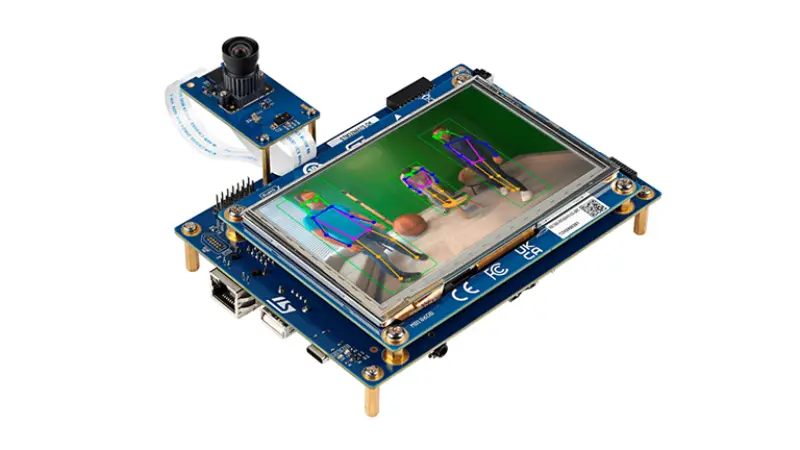

BirdNET for STM32
A specialized framework for training and deploying BirdNET audio classification models on the STM32N6570-DK development board. It provides a complete pipeline from dataset preparation and TensorFlow training to optimized NPU deployment using STMicroelectronics' X-CUBE-AI tools.
onechuk: Machine Learning Powered Wii Nunchuk
A modified Nintendo Wii Nunchuk controller powered by an ESP32 running TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers. It enables gesture-based commands via the joystick, supporting multiple action profiles like BLE HID media controls and administrative functions.
SAMA5D27 Resource Sharing
A comprehensive resource repository for the Microchip SAMA5D27 Cortex-A5 MPU, providing extensive documentation and guides for Linux development, bare-metal programming, and various RTOS ports. It features in-depth tutorials for NuttX, RT-Thread, and ThreadX, including driver integration for LVGL, EtherCAT, and TensorFlow Lite.
Tensorflow Lite Micro for RT-Thread
A port of the Tensorflow Lite Micro inference framework for the RT-Thread real-time operating system. It enables the deployment of deep learning models on resource-constrained embedded systems, featuring optimizations for ARM Cortex-M cores via CMSIS-NN and support for multiple hardware platforms including STM32 and Raspberry Pi.