lwIP
startFeatures
-
Dual-stack IPv4 and IPv6 support with packet forwarding over multiple network interfaces.
-
Full TCP implementation featuring congestion control, RTT estimation, fast recovery, and fast retransmit.
-
UDP and experimental UDP-lite extensions for low-overhead transport.
-
ICMP and ICMPv6 support for network maintenance and diagnostic functions.
-
IGMP and MLDv1 support for managing multicast traffic and listener discovery.
-
Neighbor Discovery (ND) and stateless address autoconfiguration for IPv6 compliance (RFC 4861/4862).
-
Comprehensive IP addressing via DHCP, DHCPv6, AutoIP/APIPA (Zeroconf), and Address Conflict Detection (ACD).
-
DNS client including support for mDNS (Multicast DNS) responder.
-
Layered TCP (altcp) abstraction for transparent TLS integration, typically ported to mbedTLS.
-
Point-to-Point Protocol support including PPPoS (over Serial) and PPPoE (over Ethernet).
-
6LoWPAN adaptation layer for low-power wireless networks like IEEE 802.15.4 and BLE.
-
Integrated HTTP/HTTPS server with support for Server Side Includes (SSI) and CGI.
-
SNMPv2c/v3 agent with an included MIB compiler for network management.
-
MQTT client with optional TLS encryption for secure IoT messaging.
-
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) implementation for clock synchronization.
-
NetBIOS name service responder and iPerf server for network performance testing.
Architecture
lwIP is designed with a modular architecture that balances the need for a layered protocol stack with the performance requirements of resource-constrained hardware. The core stack is contained within the src directory, while platform-specific ports and optional applications reside in the contrib directory. A central feature of its architecture is the pbuf (packet buffer) structure, which allows for zero-copy data handling as packets move through the various layers of the stack, significantly reducing CPU and memory overhead.
To accommodate different system designs, lwIP provides three distinct Application Programming Interfaces (APIs):
- Raw API: A callback-based, event-driven interface that provides the highest performance and lowest memory footprint by running directly in the TCP/IP thread.
- Netconn API: A sequential, thread-safe API that requires an operating system (RTOS) and provides a simplified programming model.
- Socket API: A BSD-compatible socket layer built on top of the Netconn API, facilitating the porting of existing standard networking code.
Use Cases
This library is ideal for:
- IoT End-Nodes: Small, battery-powered sensors using 6LoWPAN or BLE to communicate with gateways.
- Industrial Automation: PLCs and industrial controllers requiring reliable TCP/IP communication for Modbus/TCP or Ethernet/IP protocols.
- Embedded Web Servers: Devices providing local configuration or monitoring dashboards via HTTP or HTTPS.
- Network Gateways: Systems bridging traffic between different physical layers, such as Ethernet to Serial (PPP) or WiFi to 6LoWPAN.
- Resource-Constrained Systems: Microcontrollers with limited RAM (e.g., 20KB-50KB) that still require a full-featured, standards-compliant network stack.
Getting Started
Developers can begin by exploring the src directory for the core protocol implementations and the contrib directory for existing ports to various hardware and operating systems. The stack requires a header file named lwipopts.h to be defined by the user, which configures the stack’s features and memory limits at compile-time. For systems using an RTOS, a system abstraction layer (sys_arch) must be implemented to handle threading and synchronization. Comprehensive self-documentation extracted from the source code is available at the official lwIP documentation site, and development is centrally managed via the Savannah Git repository.
Related Projects (201)
View All 201 Projects →
BorneoIoT: Professional Aquarium Lighting Platform
A full-stack open-source solution for smart aquarium LED control featuring ESP32-based hardware, ESP-IDF firmware, and a Flutter mobile application. It provides high-resolution PWM dimming, sunrise/sunset simulation, and efficient CoAP/CBOR communication for professional-grade lighting management.
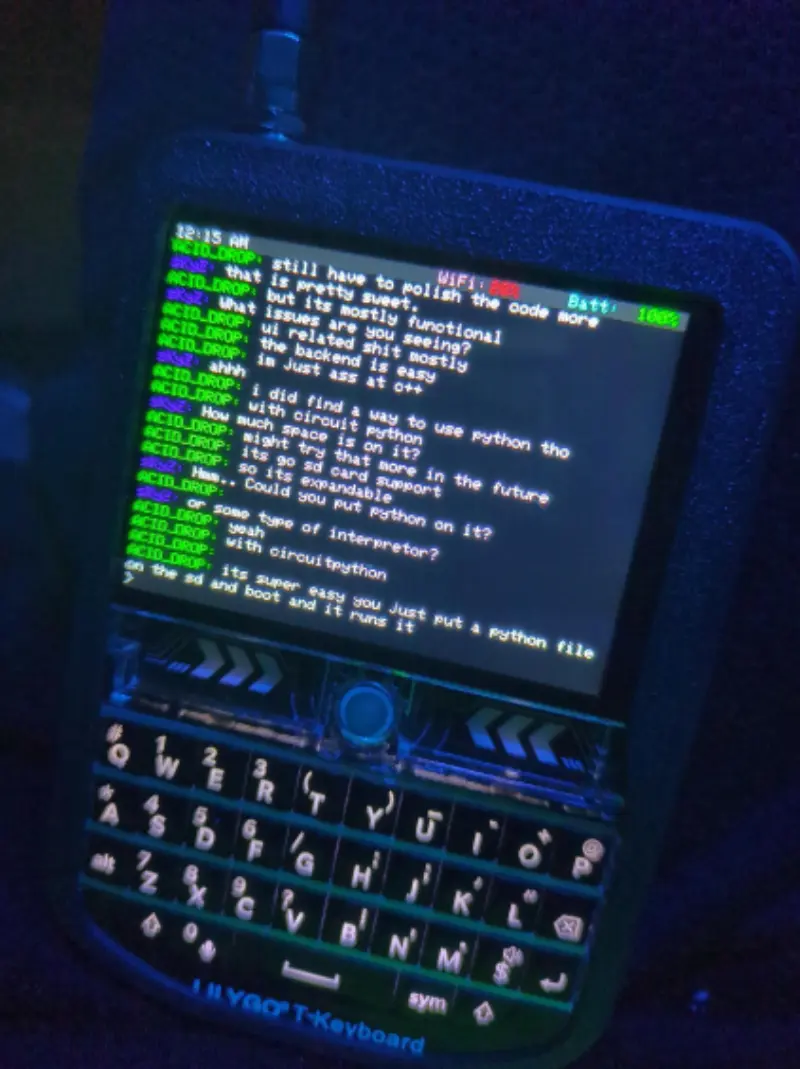
Acid Drop: Custom Firmware for LilyGo T-Deck
A custom firmware for the LilyGo T-Deck handheld device, featuring a graphical IRC client built with LVGL. It supports WiFi connectivity, audio playback, and various command-and-control features on the ESP32-S3 platform.
Modbus TCP for STM32F407
A Modbus TCP implementation for STM32F407 microcontrollers utilizing FreeRTOS and the lwIP stack. It provides a standardized TCP interface for industrial communication, supporting common read/write commands and robust error handling for automation equipment.
NFCity
An ESP32-based NFC/RFID card tool for inspecting and modifying Mifare Classic memory blocks. It utilizes an MFRC522 reader and communicates via MQTT to a Vue-based web dashboard for real-time memory manipulation and access condition configuration.
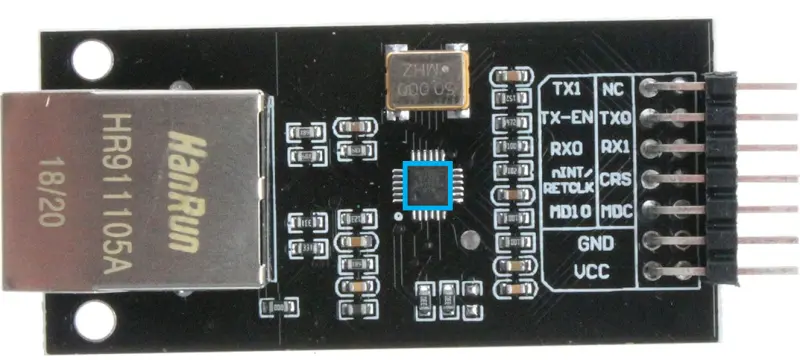
ESP32 Ethernet with LAN8720 Guide
A comprehensive guide and driver implementation for connecting the LAN8720 Ethernet PHY to an ESP32 using the ESP-IDF framework. It focuses on using the internal ESP32 PLL to generate the 50MHz reference clock, effectively avoiding common hardware conflicts with GPIO0 during the boot process.
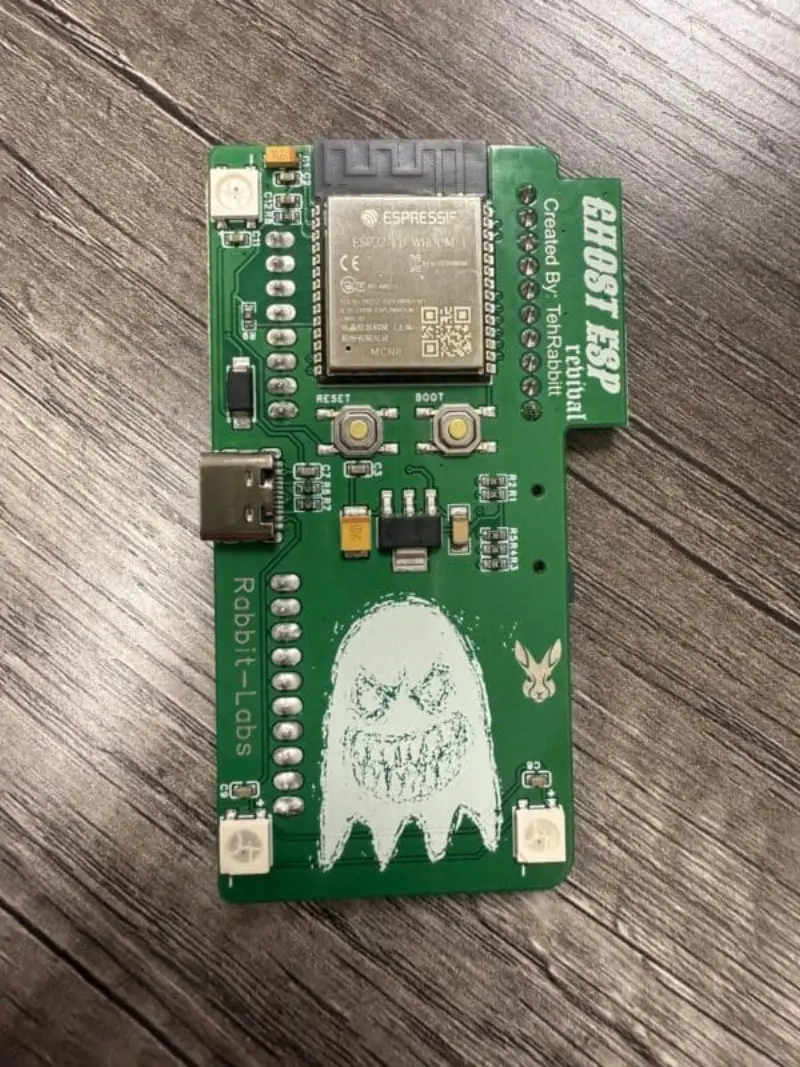

Ghost ESP
A specialized security auditing and wireless monitoring firmware for ESP32 devices. Built on the ESP-IDF framework and FreeRTOS, it provides tools for BLE wardriving, WiFi deauthentication testing, and device detection for hardware like AirTags and Flipper Zero.
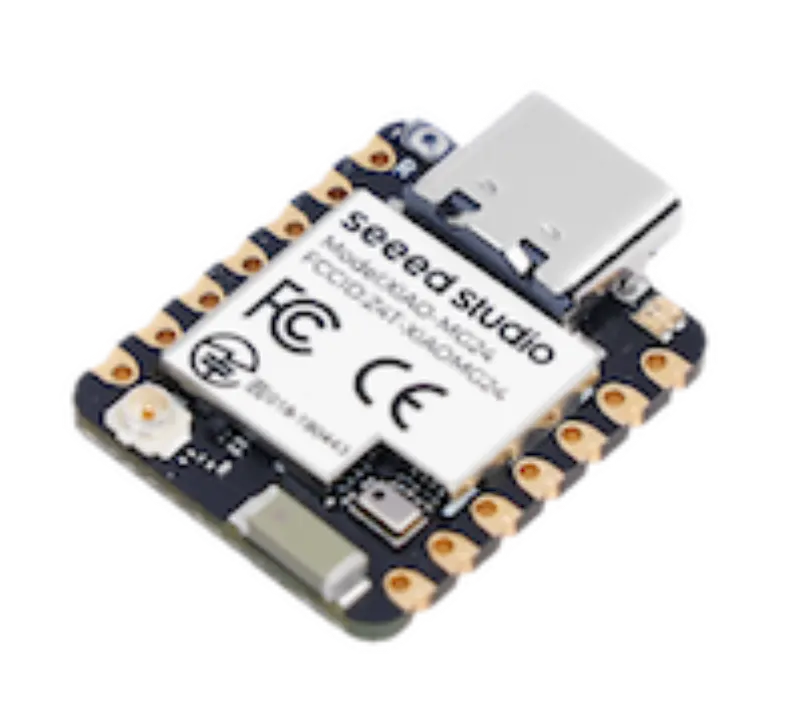

Silicon Labs Arduino Core
An Arduino core implementation for Silicon Labs microcontrollers, enabling support for Matter, BLE, and low-power wireless applications. It provides a comprehensive set of libraries and drivers for EFR32 and MGM24 series hardware, integrating Silicon Labs' Gecko SDK and FreeRTOS for advanced protocol stacks.
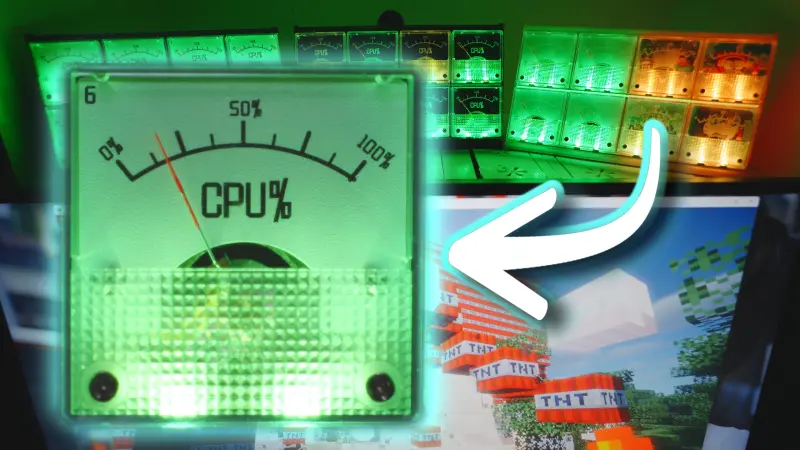
bbMonitor
An ESP32-based hardware performance monitor that visualizes computer system metrics through physical analog gauges and RGB lighting. The project leverages the Arduino framework and WebSockets to receive real-time data from a desktop companion app, providing a tactile and vintage-inspired dashboard for modern PC monitoring. It includes complete hardware design files, including PCB schematics and CAD drawings for the enclosure.